Acute Porphyria
Summary
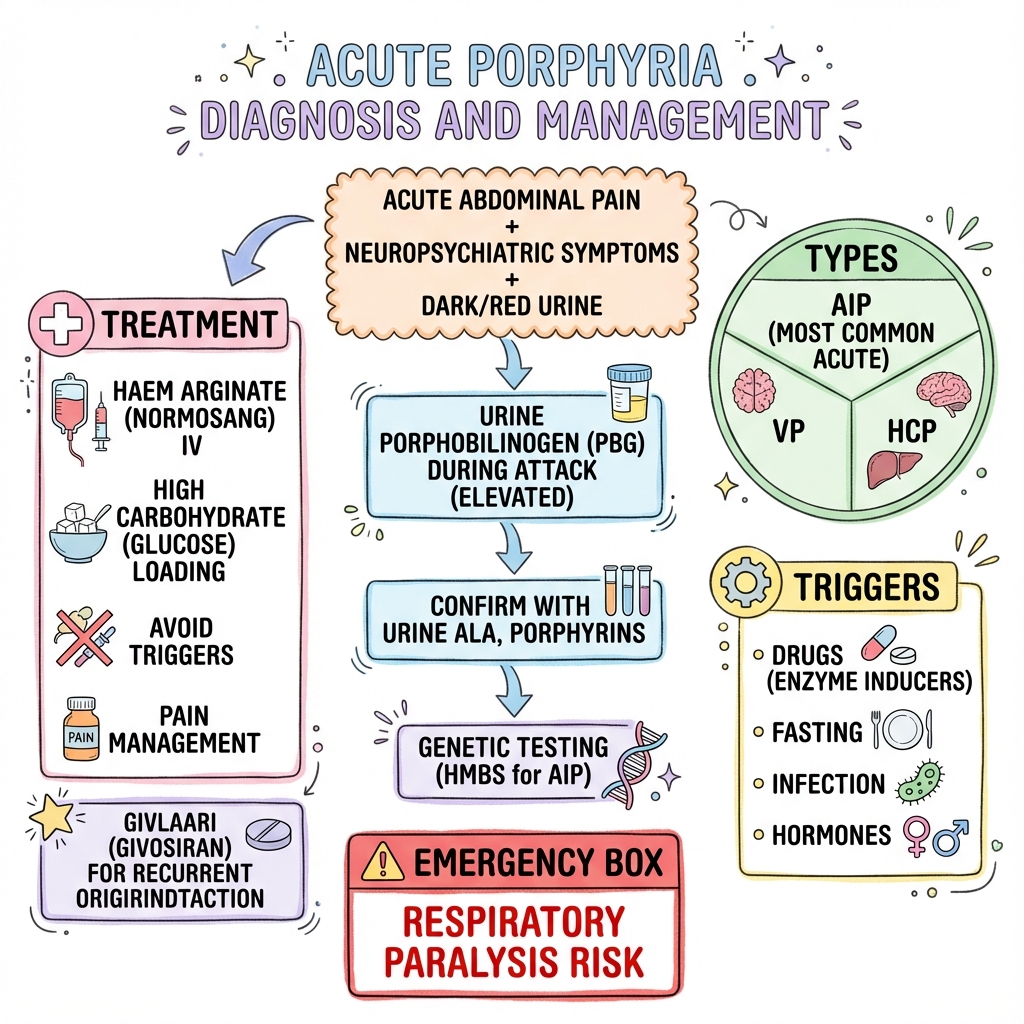
Acute porphyrias are a group of inherited metabolic disorders caused by enzyme deficiencies in the haem biosynthesis pathway. Acute intermittent porphyria (AIP) is the most common. Attacks are characterised by severe abdominal pain, neuropsychiatric symptoms, and autonomic dysfunction, often triggered by drugs, fasting, infection, or hormonal changes. Diagnosis requires detection of elevated urinary porphobilinogen (PBG) during an attack. Treatment includes IV haem arginate, high carbohydrate loading, and avoidance of triggers. Givosiran is now available for preventing recurrent attacks.
Key Facts
- Definition: Inherited haem synthesis defects causing neurovisceral attacks
- Incidence: 1-2 per 100,000; many carriers asymptomatic
- Peak Demographics: Women 20-40 (hormonal triggers)
- Pathognomonic: Elevated urine PBG during attack + dark urine
- Gold Standard Investigation: Spot urine PBG (during attack)
- First-line Treatment: IV haem arginate (Normosang)
- Prognosis: Good if diagnosed and managed; can be fatal if missed
Clinical Pearls
Diagnostic Pearl: Always test urine PBG during the attack - levels can normalise between attacks.
Emergency Pearl: Respiratory paralysis can occur - monitor closely in severe attacks.
Drug Safety Pearl: Check all drugs on porphyria-safe database before prescribing.
| Type | Gene | Features |
|---|---|---|
| AIP | HMBS | Most common; no skin manifestations |
| Variegate (VP) | PPOX | Skin photosensitivity + acute attacks |
| Hereditary Coproporphyria (HCP) | CPOX | Skin + acute attacks |
| ALA Dehydratase Deficiency | ALAD | Very rare |
Classic Triad
Other Features
Triggers
| Test | Finding |
|---|---|
| Spot urine PBG | Markedly elevated during attack |
| Urine ALA | Elevated |
| Urine porphyrins | Elevated |
| Plasma porphyrins | VP/HCP (for skin involvement) |
| Genetic testing | Confirms mutation |
Algorithm
Acute Attack
| Treatment | Notes |
|---|---|
| Haem arginate (Normosang) | 3mg/kg IV daily x 4 days |
| IV glucose | 10% dextrose if haem unavailable |
| Pain management | Opioids safe |
| Anti-emetics | Ondansetron safe |
| Treat trigger | Infection, stop unsafe drugs |
Prevention of Recurrent Attacks
| Drug | Notes |
|---|---|
| Givosiran (Givlaari) | RNAi therapy; reduces attacks (ENVISION trial) |
| Avoid triggers | Drug database, avoid fasting |
| GnRH agonists | For menstrual-related attacks |
Safe Drugs
- Paracetamol, opioids, ondansetron, beta-blockers, proton pump inhibitors
-
Puy H et al. Porphyrias. Lancet. 2010;375(9718):924-937. PMID: 20226990
-
Balwani M et al. Givosiran for Acute Intermittent Porphyria (ENVISION). N Engl J Med. 2020;382(24):2289-2301. PMID: 32521132
Viva Points
"Acute porphyria presents with severe abdominal pain, neuropsychiatric symptoms, autonomic dysfunction. Diagnose with elevated urine PBG during attack. Treat with haem arginate (Normosang). Avoid porphyria-unsafe drugs. Givosiran prevents recurrent attacks."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team