AL Amyloidosis
Summary
AL amyloidosis (immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis) is a systemic disease caused by deposition of misfolded immunoglobulin light chains produced by a clonal plasma cell population. The amyloid deposits damage organs including the heart, kidneys, liver, and nervous system. Classic presentations include nephrotic syndrome, restrictive cardiomyopathy, hepatomegaly, macroglossia, and peripheral neuropathy. Diagnosis requires tissue biopsy with Congo red staining (apple-green birefringence under polarised light) and mass spectrometry to confirm AL type. Treatment targets the underlying plasma cell clone with chemotherapy (CyBorD, daratumumab) and autologous stem cell transplant if eligible. Cardiac staging with troponin and NT-proBNP determines prognosis.
Key Facts
- Definition: Systemic amyloidosis from immunoglobulin light chain deposition
- Incidence: 10-12 per million per year
- Peak Demographics: 60-70 years; slight male predominance
- Pathognomonic: Congo red birefringence + mass spec confirmation + clonal light chain
- Gold Standard Investigation: Tissue biopsy + typing + serum free light chains
- First-line Treatment: CyBorD +/- daratumumab; ASCT if eligible
- Prognosis: Cardiac stage determines survival (months to years)
Clinical Pearls
Diagnostic Pearl: Fat pad aspirate is 80% sensitive and avoids organ biopsy in many cases.
Cardiac Pearl: "Low voltage" ECG with increased wall thickness on echo = cardiac amyloid until proven otherwise.
Treatment Pearl: Daratumumab-based regimens (ANDROMEDA trial) are now standard for newly diagnosed AL.
Organ Manifestations
| Organ | Manifestation |
|---|---|
| Heart | Restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, arrhythmias |
| Kidney | Nephrotic syndrome, progressive CKD |
| Liver | Hepatomegaly, elevated ALP |
| Nerve | Peripheral and autonomic neuropathy |
| Soft tissue | Macroglossia, periorbital purpura, carpal tunnel |
| GI | Diarrhoea, malabsorption |
| Test | Finding |
|---|---|
| Serum free light chains | Abnormal kappa:lambda ratio |
| SPEP/UPEP + immunofixation | M-protein (often small or absent) |
| Tissue biopsy | Congo red positive; apple-green birefringence |
| Mass spectrometry | Confirms AL type |
| NT-proBNP/troponin | Cardiac staging |
| Echocardiography | Increased wall thickness, diastolic dysfunction |
| Cardiac MRI | Late gadolinium enhancement; poor nulling |
Staging (Mayo 2012)
| Stage | NT-proBNP | Troponin | dFLC | Median Survival |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Normal | Normal | Low | 94 months |
| II | 1 abnormal | 40 months | ||
| III | 2 abnormal | 14 months | ||
| IV | All abnormal | High | 6 months |
Algorithm
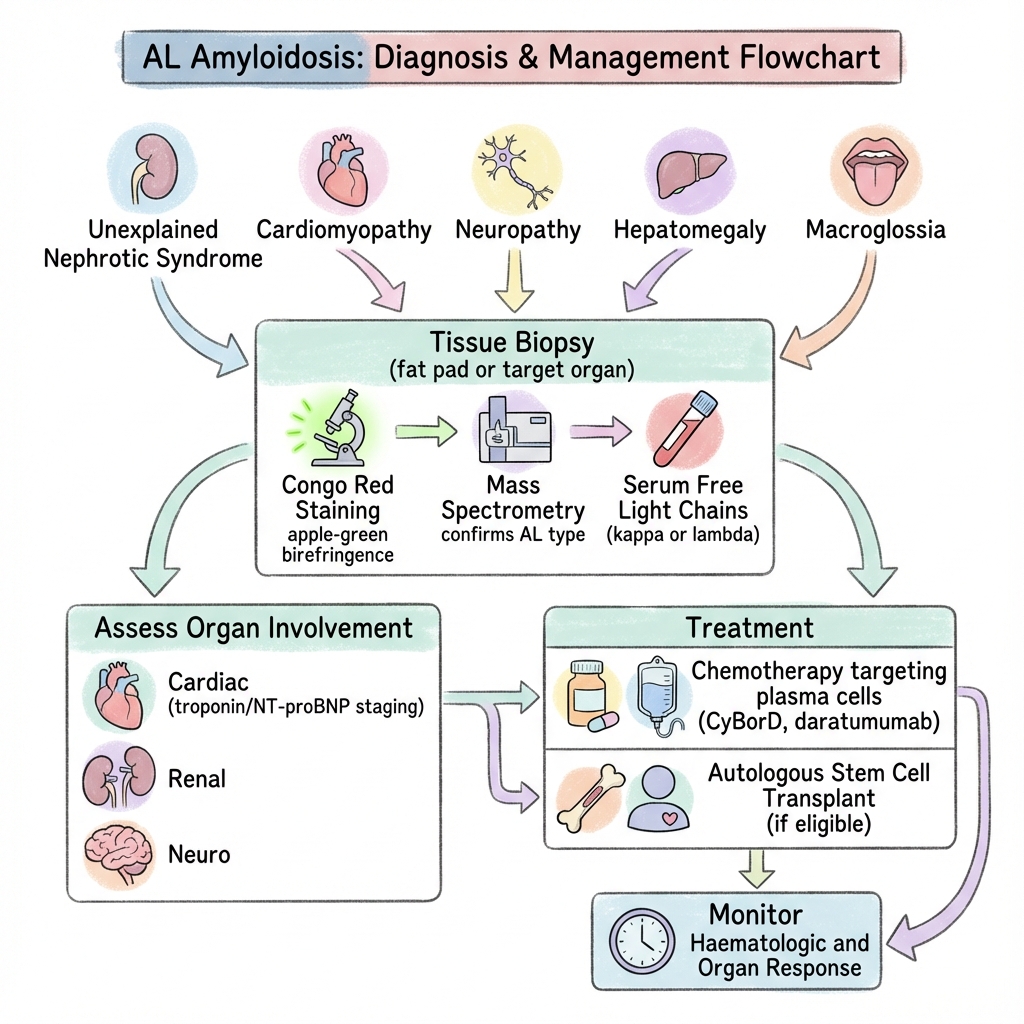
Chemotherapy
| Regimen | Notes |
|---|---|
| Dara-CyBorD | Daratumumab + cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, dexamethasone (ANDROMEDA) |
| CyBorD | Standard if dara unavailable |
| Bortezomib-based | Most effective against plasma cells |
Stem Cell Transplant
- Eligible patients (younger, limited organ involvement)
- Improves long-term outcomes
Supportive Care
- Diuretics for heart failure (careful)
- Avoid ACEi, beta-blockers, digoxin in cardiac AL
- Midodrine for autonomic hypotension
-
Dispenzieri A et al. Treatment of AL Amyloidosis: Mayo Stratification. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012;87(8):783-792. PMID: 22801936
-
Kastritis E et al. Daratumumab-Based Treatment for AL Amyloidosis (ANDROMEDA). N Engl J Med. 2021;385(1):46-58. PMID: 34192431
Viva Points
"AL amyloidosis is light chain deposition from plasma cell clone. Diagnose with biopsy (Congo red), mass spec, free light chains. Stage with cardiac biomarkers. Treat with daratumumab-based chemotherapy (ANDROMEDA). Transplant if eligible."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team