Carcinoid Syndrome and Neuroendocrine Tumours
Summary
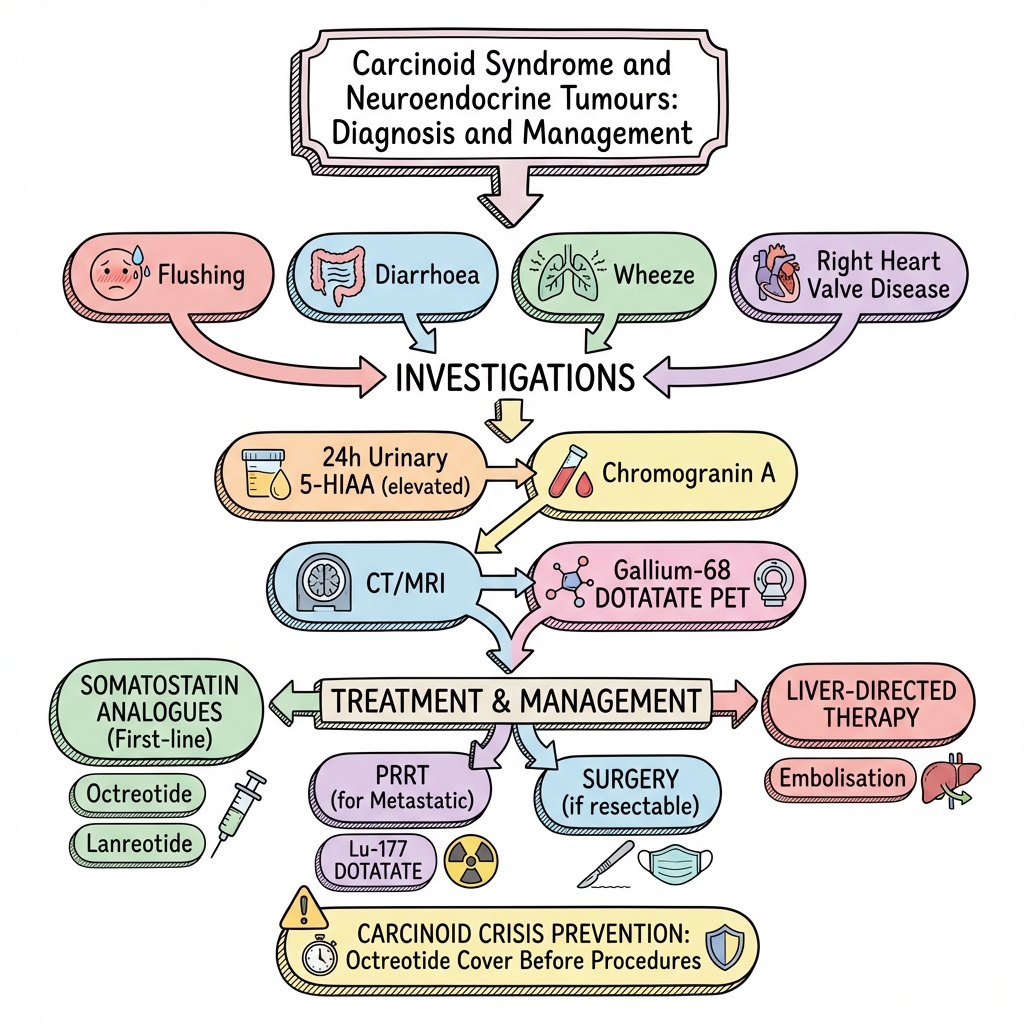
Neuroendocrine tumours (NETs) arise from neuroendocrine cells throughout the body, most commonly in the GI tract and lungs. Carcinoid syndrome occurs when tumours (usually with liver metastases) secrete vasoactive substances, primarily serotonin, into the systemic circulation. Classic features include flushing, diarrhoea, bronchospasm, and right-sided heart valve disease (carcinoid heart). Diagnosis involves measuring urinary 5-HIAA and chromogranin A, with imaging using CT and Gallium-68 DOTATATE PET. Treatment includes somatostatin analogues (octreotide, lanreotide), liver-directed therapy, and peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT).
Key Facts
- Definition: Tumours of neuroendocrine cells; syndrome from vasoactive secretion
- Incidence: 5-7 per 100,000 per year (increasing with incidental detection)
- Peak Demographics: 50-70 years
- Pathognomonic: Flushing + diarrhoea + elevated 5-HIAA
- Gold Standard Investigation: 24h urinary 5-HIAA + Ga-68 DOTATATE PET
- First-line Treatment: Somatostatin analogues (octreotide LAR, lanreotide)
- Prognosis: Variable; low-grade NETs have good survival
Clinical Pearls
Diagnostic Pearl: Carcinoid syndrome requires liver metastases (or primary draining outside portal system) to bypass hepatic metabolism.
Emergency Pearl: Carcinoid crisis (severe flushing, hypotension) can be triggered by anaesthesia/surgery. Give octreotide cover.
Treatment Pearl: CLARINET and PROMID trials established somatostatin analogues as antiproliferative.
Carcinoid Syndrome
| Feature | Mechanism |
|---|---|
| Flushing | Serotonin, histamine, bradykinin |
| Diarrhoea | Serotonin |
| Bronchospasm | Histamine, bradykinin |
| Carcinoid heart disease | Serotonin fibrosis of right heart valves |
NET Without Syndrome
| Test | Finding |
|---|---|
| 24h urinary 5-HIAA | Elevated (avoid tryptophan foods) |
| Chromogranin A | Elevated (non-specific) |
| CT/MRI | Tumour localisation |
| Ga-68 DOTATATE PET | Somatostatin receptor imaging |
| Echocardiography | Right heart valve thickening/regurgitation |
Algorithm
Somatostatin Analogues
| Drug | Dose |
|---|---|
| Octreotide LAR | 20-30mg IM monthly |
| Lanreotide | 120mg SC monthly |
Other Treatments
| Therapy | Indication |
|---|---|
| Surgery | Resectable primary/metastases |
| Liver-directed (TACE, ablation) | Unresectable liver metastases |
| PRRT (Lu-177 DOTATATE) | NETTER-1 trial; somatostatin receptor positive |
| Telotristat | Add-on for diarrhoea (TELESTAR) |
| Targeted therapy | Everolimus (RADIANT trials) |
Carcinoid Crisis Prevention
- Octreotide 100-500mcg SC/IV before procedures
-
Rinke A et al. Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Prospective, Randomized Study on the Effect of Octreotide LAR in NETs (PROMID). J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(28):4656-4663. PMID: 19704057
-
Strosberg J et al. 177Lu-Dotatate plus Long-Acting Octreotide for Midgut NETs (NETTER-1). N Engl J Med. 2017;376(2):125-135. PMID: 28076709
Viva Points
"NETs arise from neuroendocrine cells. Carcinoid syndrome = flushing, diarrhoea, bronchospasm with liver mets. Diagnose with 5-HIAA, chromogranin A, Ga-68 PET. Treat with somatostatin analogues (PROMID, CLARINET), PRRT (NETTER-1)."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team