Dermatomyositis
Summary
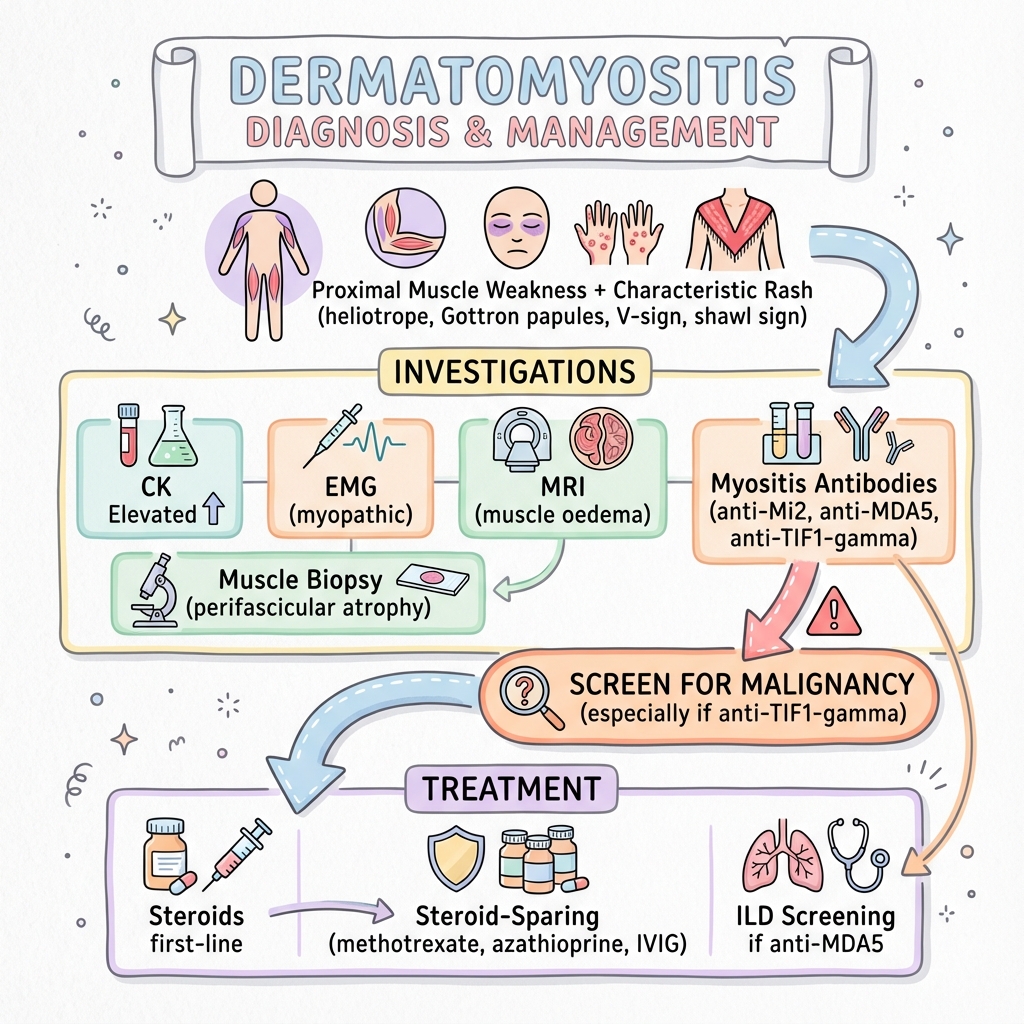
Dermatomyositis (DM) is an idiopathic inflammatory myopathy characterised by proximal muscle weakness and distinctive cutaneous manifestations. Key skin findings include heliotrope rash (violaceous periorbital discolouration), Gottron papules (scaly erythematous papules over knuckles), V-sign, and shawl sign. DM is associated with increased malignancy risk, particularly in adults with anti-TIF1-gamma antibodies. Myositis-specific antibodies help predict phenotype and complications (anti-MDA5 associated with rapidly progressive ILD). Treatment involves corticosteroids and steroid-sparing agents.
Key Facts
- Definition: Inflammatory myopathy with characteristic skin features
- Incidence: 1-10 per million per year
- Peak Demographics: Bimodal (children 5-15, adults 40-60); F greater than M
- Pathognomonic: Gottron papules + heliotrope rash + proximal weakness
- Gold Standard Investigation: Clinical + CK + EMG + MRI + biopsy + antibodies
- First-line Treatment: Corticosteroids + steroid-sparing agents
- Malignancy Risk: 15-30% in adults; screen all
Clinical Pearls
Diagnostic Pearl: Anti-TIF1-gamma is strongly associated with malignancy - comprehensive cancer screening required.
Emergency Pearl: Anti-MDA5 positive dermatomyositis can cause rapidly progressive ILD with high mortality.
Treatment Pearl: IVIG is effective for refractory skin and muscle disease.
Cutaneous Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Heliotrope rash | Violaceous periorbital oedema/discolouration |
| Gottron papules | Erythematous scaly plaques over knuckles |
| Gottron sign | Erythema over extensor surfaces |
| V-sign | Erythema over anterior chest |
| Shawl sign | Erythema over upper back/shoulders |
| Mechanic's hands | Hyperkeratotic fissured fingers |
Muscle Features
Extramuscular
| Test | Finding |
|---|---|
| CK | Elevated (may be normal in amyopathic DM) |
| EMG | Myopathic changes |
| MRI muscle | Oedema in affected muscles |
| Muscle biopsy | Perifascicular atrophy (characteristic) |
Myositis-Specific Antibodies
| Antibody | Association |
|---|---|
| Anti-Mi2 | Classic DM; good prognosis |
| Anti-TIF1-gamma | Malignancy; adult DM |
| Anti-MDA5 | Rapidly progressive ILD; amyopathic |
| Anti-NXP2 | Calcinosis; juvenile DM |
| Anti-SAE | Skin-predominant |
Malignancy Screening
- CT chest/abdomen/pelvis
- Age-appropriate cancer screening
- Consider PET-CT
Algorithm
First-Line
| Drug | Dose |
|---|---|
| Prednisolone | High-dose 1mg/kg, taper over months |
Steroid-Sparing
| Drug | Notes |
|---|---|
| Methotrexate | First-line steroid-sparing |
| Azathioprine | Alternative |
| Mycophenolate | ILD-associated |
| IVIG | Refractory skin/muscle |
| Rituximab | Refractory cases |
ILD Management
- Anti-MDA5: Aggressive immunosuppression (cyclophosphamide, tacrolimus)
- Screen all patients with PFTs
-
Dalakas MC. Inflammatory Muscle Diseases. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(18):1734-1747. PMID: 25923553
-
Lundberg IE et al. 2017 EULAR/ACR Classification Criteria for Adult and Juvenile Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(12):1955-1964. PMID: 29079590
Viva Points
"Dermatomyositis: proximal weakness + characteristic rash (heliotrope, Gottron). Check CK, EMG, MRI, biopsy. Anti-TIF1-gamma = malignancy screen. Anti-MDA5 = ILD risk. Treat with steroids + steroid-sparing agents."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team