Epilepsy
Summary
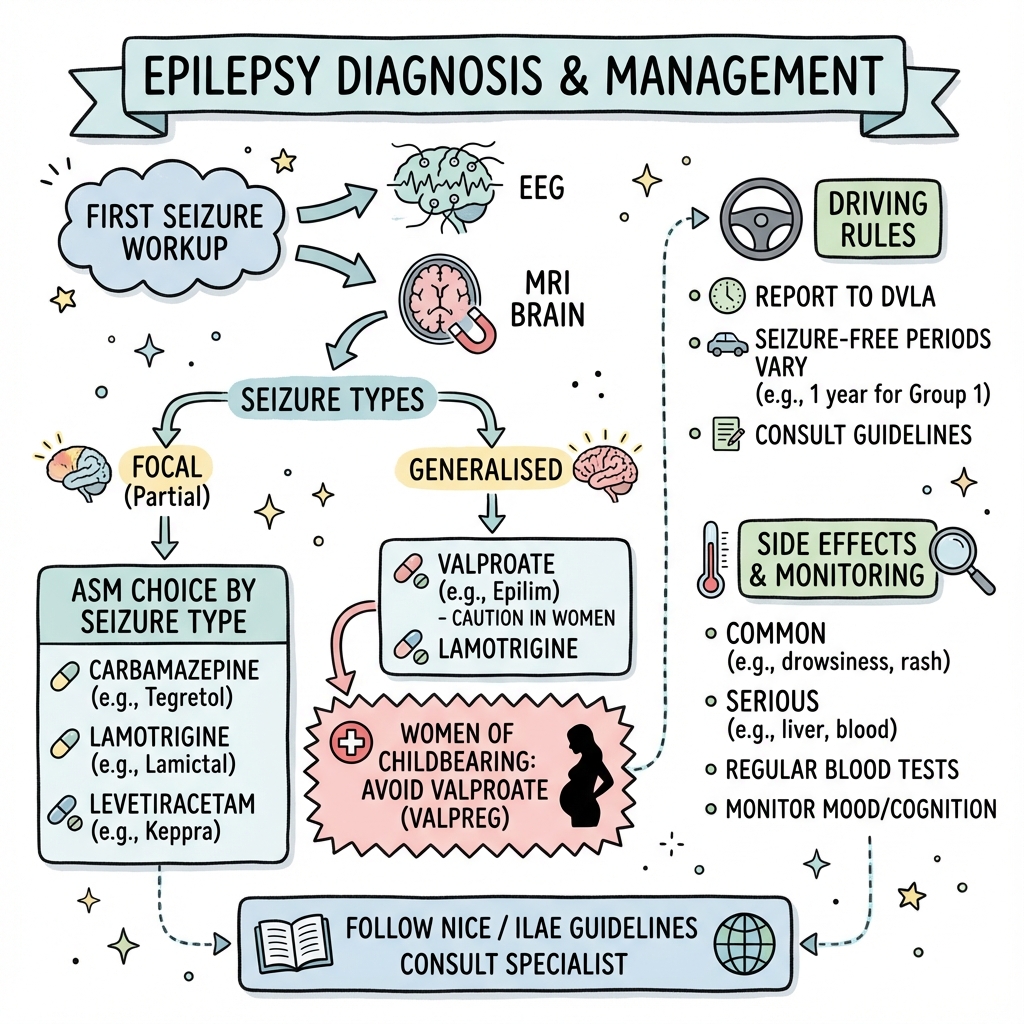
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological condition characterised by recurrent unprovoked seizures. Seizures are classified as focal or generalised. Diagnosis requires clinical history, EEG, and MRI. Anti-seizure medications (ASMs) are the mainstay of treatment, chosen based on seizure type and patient factors. Special considerations apply to women of childbearing potential (avoid valproate).
Key Facts
- Definition: Two or more unprovoked seizures 24h+ apart
- Incidence: 0.5-1% prevalence
- Pathognomonic: Witnessed seizure + EEG abnormalities
- Gold Standard Investigation: EEG + MRI brain
- First-line Treatment: ASM based on seizure type
- Prognosis: 70% controlled with first/second ASM
Clinical Pearls
Valproate Pearl: Avoid in women of childbearing potential - teratogenic (VALPREG).
First Seizure Pearl: Not all first seizures need ASM - assess risk factors.
Driving Pearl: Must be seizure-free 12 months to drive (or longer for HGV).
| Type | Features |
|---|---|
| Focal | Starts in one hemisphere; aware or impaired awareness |
| Generalised | Involves both hemispheres from onset; tonic-clonic, absence, myoclonic |
Algorithm
ASM Choice
| Seizure Type | First-Line |
|---|---|
| Focal | Carbamazepine, lamotrigine, levetiracetam |
| Generalised tonic-clonic | Valproate*, lamotrigine |
| Absence | Valproate*, ethosuximide |
| Myoclonic | Valproate*, levetiracetam |
*Avoid valproate in women of childbearing potential
-
NICE guideline NG217. Epilepsies in children, young people and adults. 2022.
-
Kwan P et al. Definition of drug resistant epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2010;51(6):1069-1077. PMID: 19889013
Viva Points
"Epilepsy: focal vs generalised. ASM by seizure type. Avoid valproate in women of childbearing potential. Driving: 12 months seizure-free."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team