Polyarteritis Nodosa
Summary
Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) is a necrotising vasculitis affecting medium-sized arteries. Unlike ANCA-associated vasculitis, PAN is ANCA-negative and does not typically involve the lungs or glomeruli. It presents with constitutional symptoms, skin involvement (livedo reticularis, nodules), mononeuritis multiplex, renal (hypertension, infarcts), and GI manifestations (mesenteric ischaemia). Historically associated with hepatitis B, though incidence has declined with vaccination. Diagnosis is by angiography (microaneurysms) or tissue biopsy. Treatment involves steroids and cyclophosphamide; HepB-associated PAN requires antivirals.
Key Facts
- Definition: ANCA-negative medium-vessel necrotising vasculitis
- Incidence: 2-9 per million per year
- Peak Demographics: 40-60 years; M greater than F
- Pathognomonic: Microaneurysms on angiography + ANCA negative
- Gold Standard Investigation: Angiography or tissue biopsy
- First-line Treatment: Steroids +/- cyclophosphamide
- Prognosis: Good with treatment; 90% 5-year survival
Clinical Pearls
Diagnostic Pearl: PAN is ANCA-negative - this differentiates it from GPA/MPA.
Association Pearl: Always check HBV serology - HepB-associated PAN requires different treatment.
Angiographic Pearl: Microaneurysms affecting renal, hepatic, mesenteric arteries are characteristic.
| System | Features |
|---|---|
| Constitutional | Fever, weight loss, fatigue |
| Skin | Livedo reticularis, nodules, ulcers |
| Nervous | Mononeuritis multiplex (foot/wrist drop) |
| Renal | Hypertension, renal infarcts (NOT glomerulonephritis) |
| GI | Abdominal pain, mesenteric ischaemia, GI bleeding |
| Cardiac | Pericarditis, MI (coronary arteritis) |
| Testicular | Orchitis |
| Test | Finding |
|---|---|
| ANCA | Negative (MUST be negative for PAN) |
| HBV serology | Positive in 10-30% |
| CRP/ESR | Elevated |
| Angiography | Microaneurysms, vessel stenosis |
| Biopsy | Medium-vessel necrotising vasculitis |
Algorithm
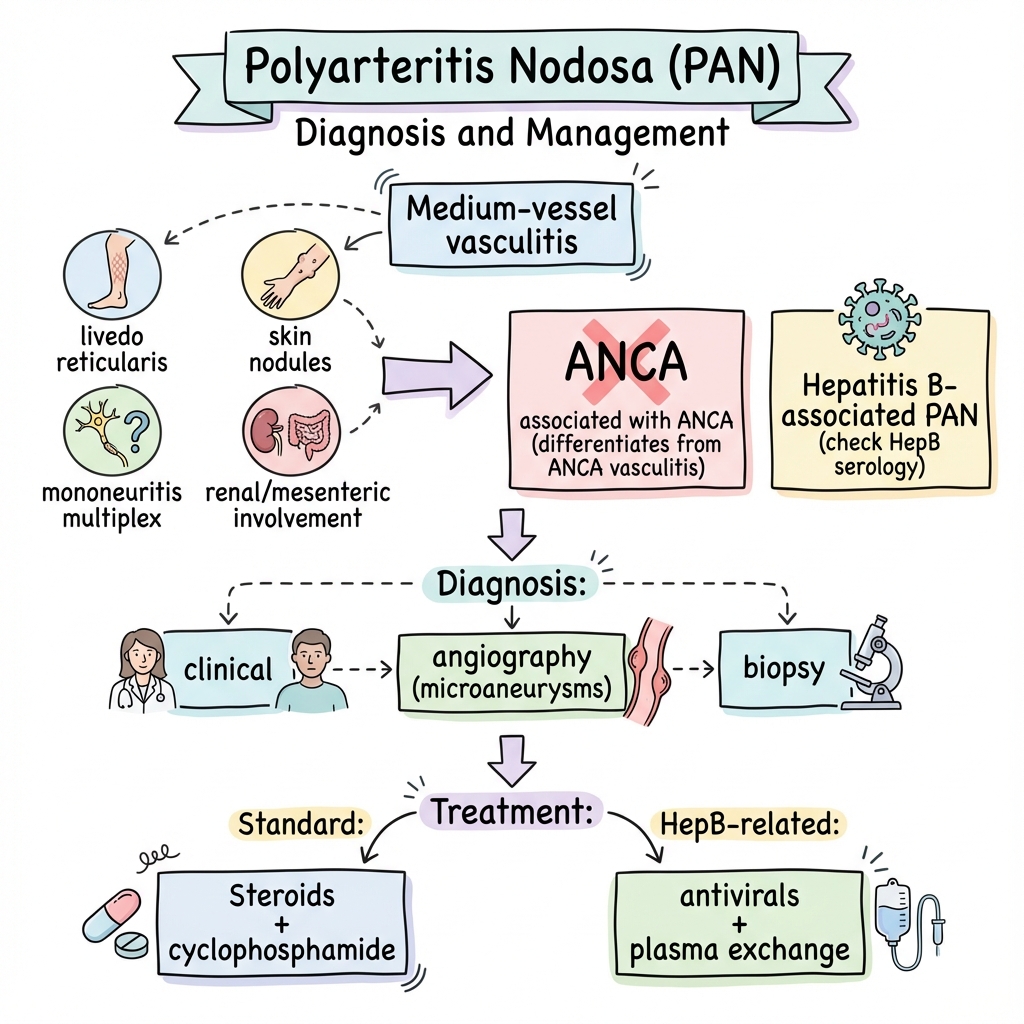
Non-HBV PAN
| Regimen | Notes |
|---|---|
| Steroids | Prednisolone 1mg/kg |
| Cyclophosphamide | For severe/organ-threatening |
| Azathioprine | Maintenance |
HBV-Associated PAN
| Regimen | Notes |
|---|---|
| Antivirals | Entecavir, tenofovir |
| Plasma exchange | Short-term steroids |
-
Jennette JC et al. 2012 Revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(1):1-11. PMID: 23045170
-
De Virgilio A et al. Polyarteritis nodosa: Clinical manifestations and treatment. Autoimmun Rev. 2016;15(6):538-542. PMID: 26876384
Viva Points
"PAN is ANCA-negative medium-vessel vasculitis. Features: livedo, mononeuritis multiplex, renal/mesenteric involvement. NOT lung/glomerular like ANCA vasculitis. Diagnose with angiography (microaneurysms). Check HBV. Treat with steroids + cyclophosphamide."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team