Septic Arthritis
Summary
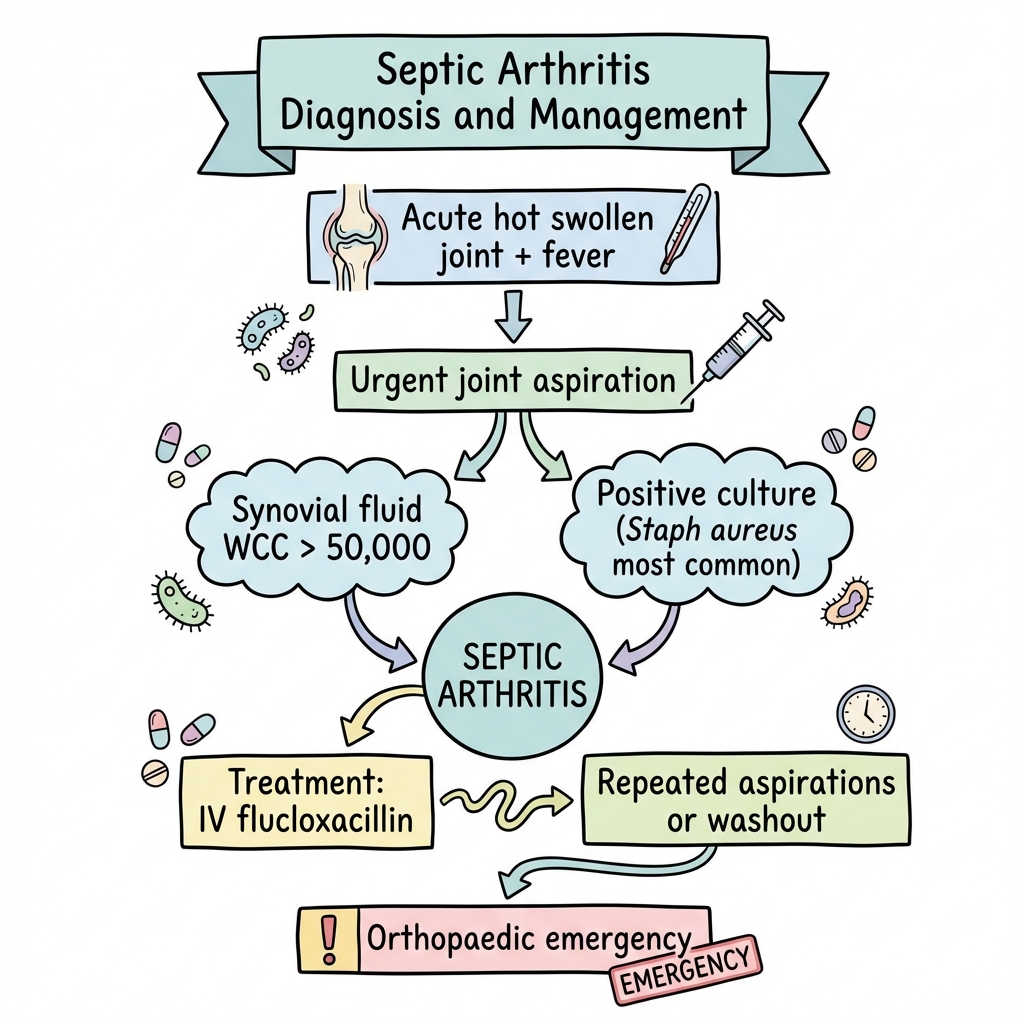
Septic arthritis is a medical emergency characterised by bacterial infection of a joint, most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Delay in treatment leads to irreversible joint destruction. Patients present with acute onset of a hot, swollen, painful joint with reduced range of movement. Diagnosis requires urgent joint aspiration with synovial fluid analysis (WCC greater than 50,000, neutrophil predominance). Treatment involves empirical IV antibiotics and joint drainage (repeated aspiration or surgical washout).
Key Facts
- Definition: Bacterial infection within a joint
- Incidence: 2-10 per 100,000 per year
- Peak Demographics: Elderly, immunocompromised, prosthetic joints
- Pathognomonic: Hot swollen joint + purulent synovial fluid
- Gold Standard Investigation: Joint aspiration + culture
- First-line Treatment: IV flucloxacillin + urgent orthopaedic input
- Prognosis: Good if treated early; permanent damage if delayed
Clinical Pearls
Emergency Pearl: This is a medical emergency - delays destroy cartilage within 24-48h.
Aspiration Pearl: Aspirate BEFORE antibiotics if possible, but do not delay treatment.
Organism Pearl: Staph aureus is most common; gonococcus in young sexually active.
Algorithm
Antibiotics
| Regimen | Drugs |
|---|---|
| Empirical | Flucloxacillin 2g QDS IV + Gentamicin |
| Penicillin allergy | Vancomycin |
| Gonococcal | Ceftriaxone 1g OD |
Drainage
- Repeated needle aspiration
- Arthroscopic washout
- Open surgical drainage if needed
- Coakley G et al. BSR and BHPR Guideline for Acute Hot Swollen Joint. Rheumatology. 2006;45(8):1039-1041. PMID: 16829534
Viva Points
"Septic arthritis: orthopaedic emergency. Aspirate urgently - WCC greater than 50,000. Staph aureus most common. IV flucloxacillin + drainage."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team