Atrial Fibrillation
Summary
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia, characterised by irregular atrial activation and absent coordinated atrial contraction. ECG shows irregularly irregular rhythm with absent P waves. Management has two pillars: rate or rhythm control, and anticoagulation for stroke prevention. CHA2DS2-VASc score guides anticoagulation decisions, with DOACs preferred over warfarin. Unstable AF requires immediate DC cardioversion.
Key Facts
- Definition: Chaotic atrial activity with irregularly irregular ventricular response
- Incidence: 1-2% population; increases with age
- Pathognomonic: Irregularly irregular pulse + absent P waves
- Gold Standard Investigation: 12-lead ECG
- First-line Treatment: Rate control + anticoagulation (if indicated)
- Prognosis: 5x stroke risk without anticoagulation
Clinical Pearls
Anticoagulation Pearl: CHA2DS2-VASc 2+ (male) or 3+ (female) = DOAC indicated.
Rate vs Rhythm Pearl: Rate control is first-line for most; rhythm control for symptomatic or young.
Cardioversion Pearl: If AF less than 48h or adequately anticoagulated 3+ weeks = safe to cardiovert.
| Type | Definition |
|---|---|
| Paroxysmal | Self-terminates within 7 days |
| Persistent | Sustained greater than 7 days or requires cardioversion |
| Long-standing persistent | Greater than 12 months |
| Permanent | Accepted; no rhythm control attempted |
| Risk Factor | Points |
|---|---|
| Congestive HF | 1 |
| Hypertension | 1 |
| Age 75+ | 2 |
| Diabetes | 1 |
| Stroke/TIA/TE | 2 |
| Vascular disease | 1 |
| Age 65-74 | 1 |
| Sex (female) | 1 |
Algorithm
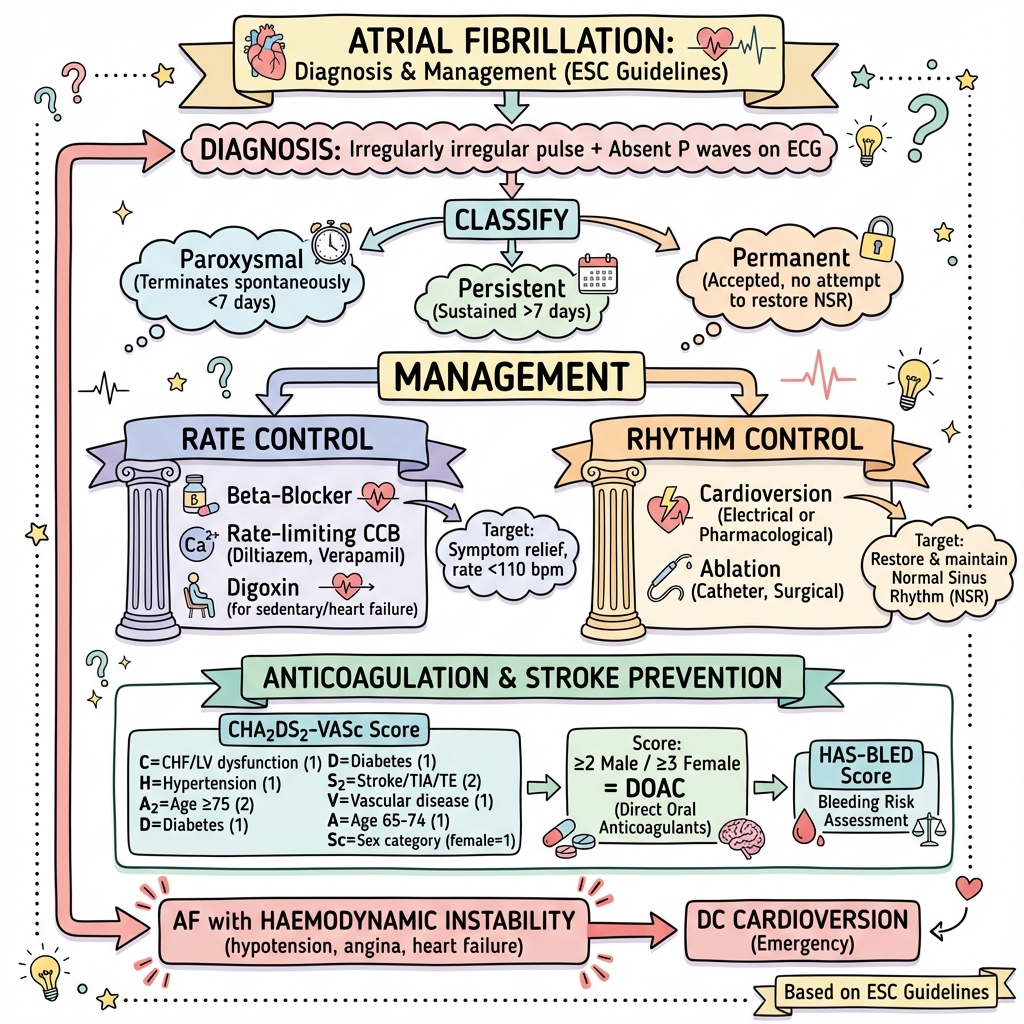
Rate Control
| Drug | Dose |
|---|---|
| Bisoprolol | 2.5-10mg OD |
| Diltiazem | 60-120mg TDS |
| Digoxin | For sedentary/HF |
Rhythm Control
- Electrical cardioversion
- Pharmacological (flecainide, amiodarone)
- Catheter ablation
Anticoagulation
| Drug | Notes |
|---|---|
| Apixaban | 5mg BD (preferred) |
| Rivaroxaban | 20mg OD |
| Edoxaban | 60mg OD |
| Warfarin | INR 2-3 (if DOACs contraindicated) |
-
Hindricks G et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(5):373-498. PMID: 32860505
-
NICE guideline NG196. Atrial fibrillation: diagnosis and management. 2021.
Viva Points
"AF: irregularly irregular, absent P waves. CHA2DS2-VASc guides anticoagulation. Rate control first-line (beta-blocker/CCB). DOAC preferred. Unstable = DC cardioversion."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team