ANCA-Associated Vasculitis
Summary
ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) comprises three small-vessel vasculitides: granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA, formerly Wegener's), microscopic polyangiitis (MPA), and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA, formerly Churg-Strauss). These conditions are characterised by necrotising vasculitis of small vessels and are associated with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA). GPA typically presents with upper and lower respiratory involvement plus glomerulonephritis. MPA affects kidneys and lungs without granulomas. EGPA is associated with asthma and eosinophilia. Treatment involves induction with steroids plus cyclophosphamide or rituximab, followed by maintenance immunosuppression.
Key Facts
- Definition: Small-vessel necrotising vasculitis associated with ANCA
- Incidence: 20-25 per million per year
- Peak Demographics: 50-70 years; slight male predominance
- ANCA Patterns: PR3-ANCA (GPA), MPO-ANCA (MPA, EGPA)
- Gold Standard Investigation: ANCA + tissue biopsy
- First-line Treatment: Steroids + cyclophosphamide or rituximab
- Prognosis: 80-90% remission; relapse common
Clinical Pearls
Diagnostic Pearl: PR3-ANCA is highly specific for GPA; MPO-ANCA is seen in MPA and EGPA. c-ANCA pattern usually correlates with PR3.
Emergency Pearl: Pulmonary-renal syndrome (haemoptysis + AKI) is a medical emergency requiring urgent plasma exchange.
Treatment Pearl: Rituximab is now preferred over cyclophosphamide for many patients (RAVE trial).
| Disease | ANCA | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| GPA | PR3 (c-ANCA) | Granulomas; ENT, lung, kidney |
| MPA | MPO (p-ANCA) | No granulomas; kidney, lung |
| EGPA | MPO (p-ANCA) | Asthma, eosinophilia, neuropathy |
GPA
MPA
EGPA
Red Flags
[!CAUTION]
- Haemoptysis with renal impairment
- Rapidly rising creatinine
- Respiratory failure
| Test | Finding |
|---|---|
| ANCA | PR3 or MPO positive |
| Urinalysis | Active sediment (RBC casts) |
| Creatinine | Elevated if renal involvement |
| CXR/CT | Nodules, cavities, infiltrates |
| Biopsy | Necrotising vasculitis, granulomas (GPA) |
Algorithm
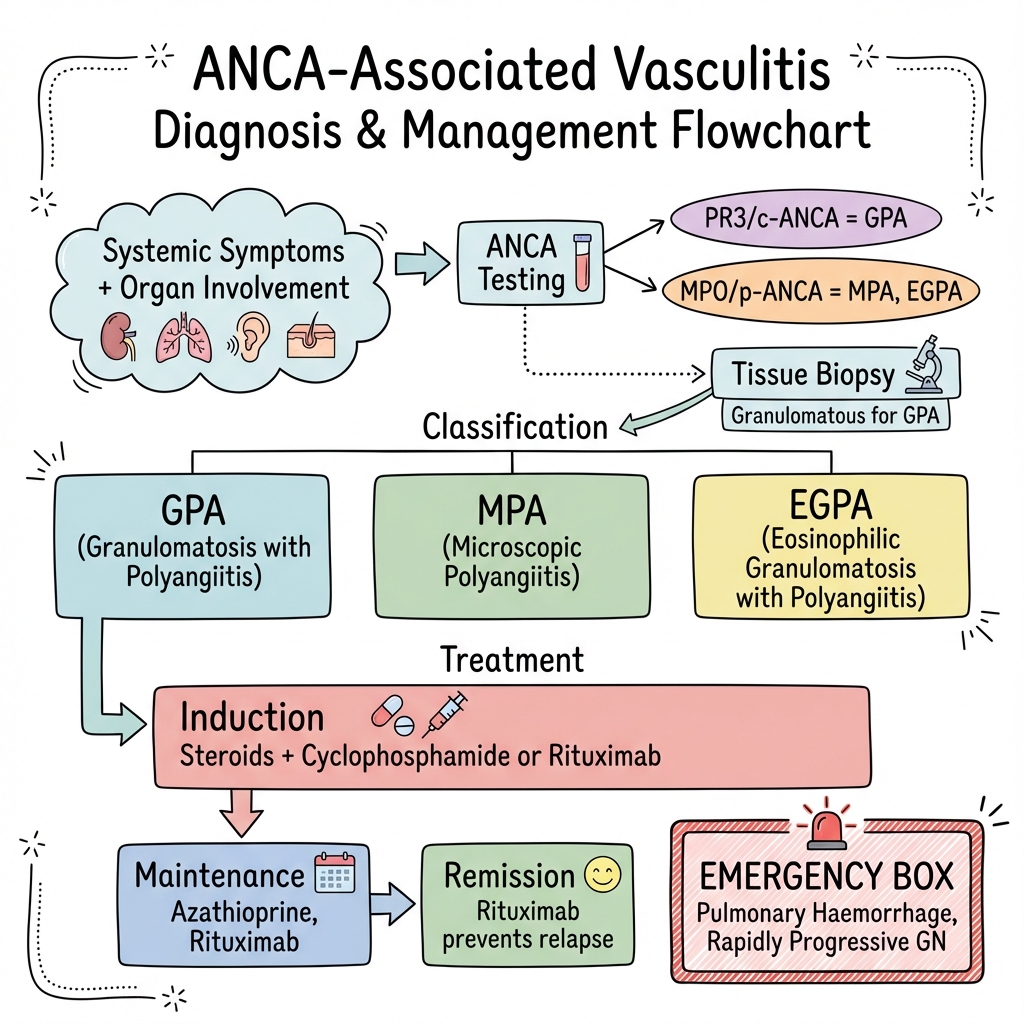
Induction
| Regimen | Dose | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Steroids | Methylpred 500mg-1g x3, then pred 1mg/kg | Taper over months |
| Cyclophosphamide | IV pulses or oral | Traditional |
| Rituximab | 375mg/m2 weekly x4 or 1g x2 | Preferred (RAVE trial) |
Maintenance
| Drug | Notes |
|---|---|
| Azathioprine | Traditional |
| Rituximab | Preferred; reduces relapse (MAINRITSAN) |
| Methotrexate | Alternative |
Severe Disease
- Plasma exchange for pulmonary haemorrhage or severe renal disease
-
Stone JH et al. Rituximab versus Cyclophosphamide for ANCA-Associated Vasculitis (RAVE). N Engl J Med. 2010;363(3):221-232. PMID: 20647199
-
Guillevin L et al. Rituximab vs Azathioprine for Maintenance in ANCA Vasculitis (MAINRITSAN). JAMA. 2014;312(17):1776-1785. PMID: 25358561
Viva Points
"ANCA vasculitis comprises GPA (PR3), MPA (MPO), EGPA (MPO + asthma + eosinophilia). Treat with steroids + rituximab or cyclophosphamide induction, then rituximab maintenance. Plasma exchange for pulmonary-renal syndrome."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team