Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Summary
Cirrhosis is the end-stage of chronic liver disease characterised by fibrosis and nodular regeneration. It may be compensated or decompensated (ascites, variceal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy). Child-Pugh and MELD scores assess severity. Management involves treating the underlying cause, managing complications, and assessing for liver transplantation.
Key Facts
- Definition: Chronic liver injury with fibrosis and architectural distortion
- Incidence: 250+ per 100,000
- Pathognomonic: Stigmata of CLD + portal hypertension
- Gold Standard Investigation: Fibroscan, liver biopsy
- First-line Treatment: Treat cause; manage complications
- Prognosis: Child A 5-year survival 80%; Child C 35%
Clinical Pearls
Compensated Pearl: Compensated cirrhosis can be stable for years - treat cause.
Decompensation Pearl: Ascites, HE, or variceal bleed = decompensated = transplant referral.
HCC Pearl: Ultrasound every 6 months for HCC surveillance.
| Parameter | 1 point | 2 points | 3 points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bilirubin | less than 34 | 34-50 | greater than 50 |
| Albumin | greater than 35 | 28-35 | less than 28 |
| INR | less than 1.7 | 1.7-2.3 | greater than 2.3 |
| Ascites | None | Mild | Moderate-severe |
| HE | None | Grade 1-2 | Grade 3-4 |
- Class A: 5-6, Class B: 7-9, Class C: 10-15
Algorithm
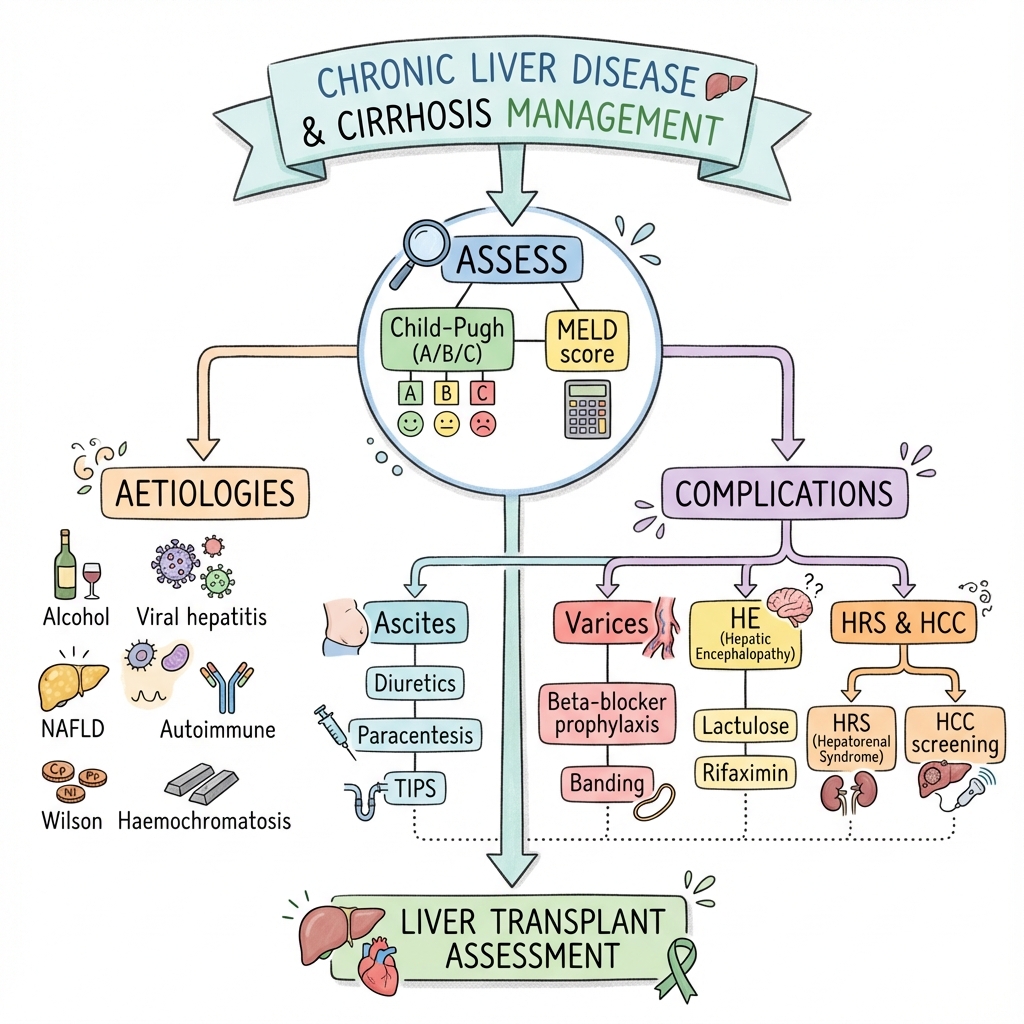
Complications
| Complication | Treatment |
|---|---|
| Ascites | Spironolactone + furosemide, paracentesis, TIPS |
| Varices | Beta-blocker prophylaxis, banding |
| HE | Lactulose, rifaximin |
| HRS | Terlipressin + albumin |
HCC Surveillance
- USS every 6 months
- AFP (centres vary)
-
EASL. Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol. 2022.
-
NICE guideline NG50. Cirrhosis in over 16s: assessment and management. 2016.
Viva Points
"Cirrhosis: Child-Pugh A/B/C, MELD for transplant. Decompensation = ascites, HE, variceal bleed. Manage cause, complications. HCC screen every 6 months."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team