Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Summary
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening diabetic emergency characterised by the triad of hyperglycaemia, ketonaemia, and metabolic acidosis. It occurs primarily in type 1 diabetes (but can occur in T2DM) due to absolute or relative insulin deficiency. Precipitants include infection, missed insulin, and new diabetes. Treatment follows a protocolised approach: aggressive IV fluids, fixed-rate IV insulin, potassium replacement, and identification of the precipitant. Resolution is defined by ketones below 0.6 mmol/L, pH above 7.3, and bicarbonate above 15.
Key Facts
- Definition: Hyperglycaemia + ketonaemia + acidosis
- Incidence: 4-8% of T1DM patients per year
- Peak Demographics: Young adults with T1DM
- Pathognomonic: Glucose greater than 11 + ketones greater than 3 + pH less than 7.3
- Gold Standard Investigation: VBG, ketones, glucose, U and E
- First-line Treatment: 0.9% saline + insulin 0.1 units/kg/hr + K replacement
- Prognosis: Mortality less than 1% with good care
Clinical Pearls
Insulin Pearl: Never stop insulin until ketones less than 0.6 even if glucose normalises - add dextrose instead.
Potassium Pearl: K drops with insulin and fluids - replace if less than 5.5, hold insulin if less than 3.5.
Cerebral Oedema Pearl: Risk in young patients with rapid correction - headache, confusion = stop fluids, mannitol.
| Feature | Value |
|---|---|
| Blood glucose | Greater than 11 mmol/L |
| Blood ketones | Greater than 3 mmol/L |
| pH | Less than 7.3 |
| Bicarbonate | Less than 15 mmol/L |
Severity
| Criteria | Mild | Moderate | Severe |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.25-7.30 | 7.0-7.24 | Less than 7.0 |
| Bicarb | 15-18 | 10-15 | Less than 10 |
- Infection (most common)
- Missed insulin doses
- New diagnosis of diabetes
- Medications (steroids, SGLT2 inhibitors)
- MI, stroke
- Pregnancy
Algorithm
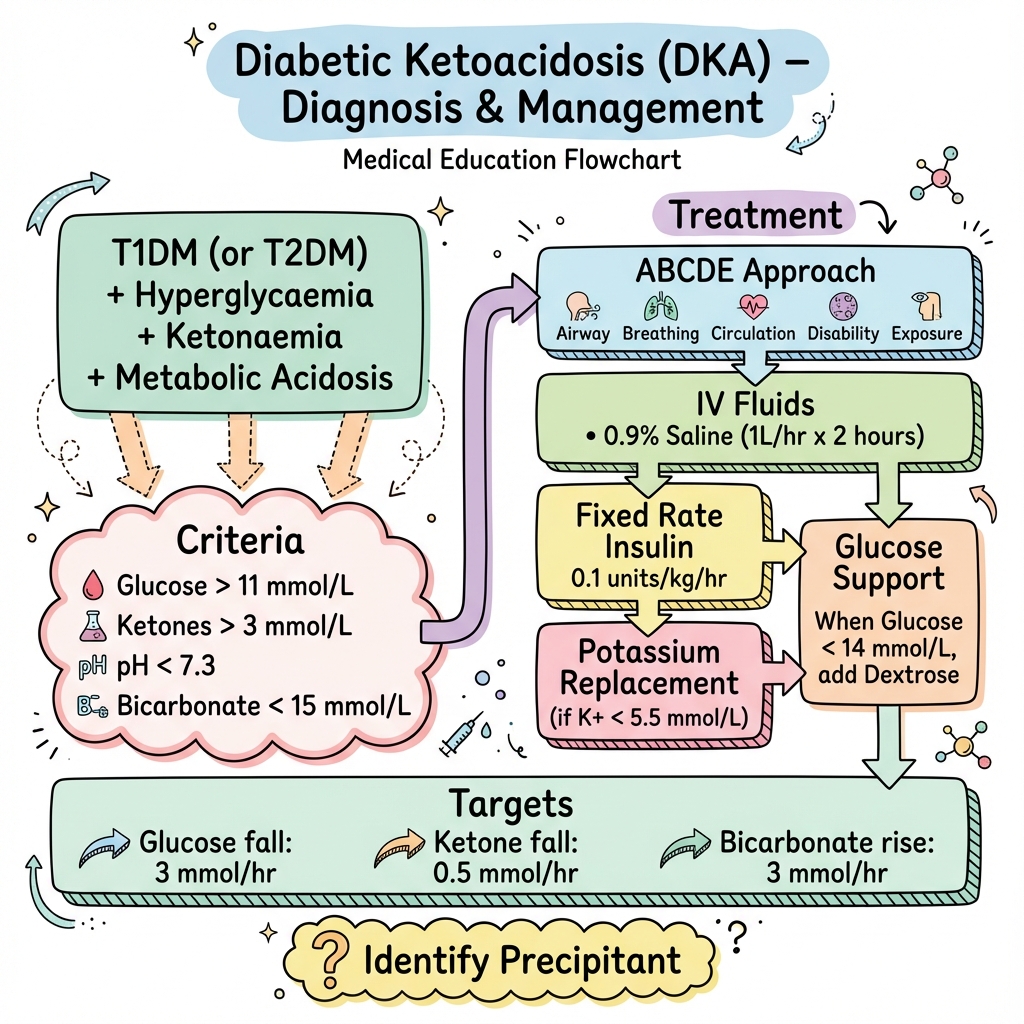
Fluids
| Time | Fluid |
|---|---|
| 0-1h | 0.9% saline 1L over 1h |
| 1-2h | 1L over 1h |
| 2-6h | 1L over 2h x2 |
| When glucose less than 14 | Add 10% dextrose |
Insulin
| Regimen | Dose |
|---|---|
| Fixed rate IV | 0.1 units/kg/hr (e.g., 50 units in 50ml) |
Potassium
| K level | Action |
|---|---|
| Less than 3.5 | Hold insulin, aggressive replacement |
| 3.5-5.5 | Replace (40mmol/L in each bag) |
| Greater than 5.5 | No replacement initially |
Targets
- Glucose: Fall 3 mmol/L/hr
- Ketones: Fall 0.5 mmol/L/hr
- Bicarb: Rise 3 mmol/L/hr
Resolution Criteria
- Ketones less than 0.6 mmol/L
- pH greater than 7.3
- Bicarb greater than 15
-
Joint British Diabetes Societies. The Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Adults. 2023. JBDS DKA Guidelines
-
Kitabchi AE et al. Hyperglycemic Crises in Adult Patients With Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(7):1335-1343. PMID: 19564476
Viva Points
"DKA: T1DM, hyperglycaemia + ketones + acidosis. JBDS protocol: 0.9% saline, fixed-rate insulin 0.1u/kg/hr, K replacement. Targets: glucose fall 3mmol/hr, ketones fall 0.5mmol/hr. Resolution: ketones less than 0.6, pH greater than 7.3."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team