Lupus Nephritis
Summary
Lupus nephritis (LN) is a major manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), affecting up to 50% of patients. It results from immune complex deposition in the glomeruli, causing inflammation and damage. Classification is based on renal biopsy using the ISN/RPS system (Classes I-VI). Proliferative nephritis (Class III/IV) requires aggressive immunosuppressive treatment with steroids plus mycophenolate or cyclophosphamide. Membranous LN (Class V) may require additional therapy. Hydroxychloroquine is protective and should be continued. Newer agents (voclosporin, belimumab) have been added to treatment arsenals.
Key Facts
- Definition: Immune-mediated renal inflammation in SLE
- Incidence: 50% of SLE patients develop renal involvement
- Peak Demographics: Young women (mirroring SLE)
- Pathognomonic: Biopsy with immune complex deposits (IgG, C3)
- Gold Standard Investigation: Renal biopsy (ISN/RPS classification)
- First-line Treatment: Steroids + mycophenolate or cyclophosphamide
- Prognosis: 5-year renal survival 80-90% with treatment
Clinical Pearls
Diagnostic Pearl: All SLE patients with proteinuria greater than 500mg/day or active sediment need renal biopsy.
Treatment Pearl: Hydroxychloroquine reduces renal flares - continue in all lupus nephritis.
Monitoring Pearl: Anti-dsDNA and complement (C3/C4) correlate with disease activity.
| Class | Description | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| I | Minimal mesangial | Supportive |
| II | Mesangial proliferative | Low-dose steroids if needed |
| III | Focal proliferative | Induction + maintenance |
| IV | Diffuse proliferative | Aggressive induction + maintenance |
| V | Membranous | If nephrotic: treat as III/IV |
| VI | Sclerosing | Supportive (dialysis/transplant) |
Features
Laboratory
| Test | Finding |
|---|---|
| Urinalysis | Proteinuria, haematuria, RBC casts |
| Anti-dsDNA | Elevated (correlates with activity) |
| Complement (C3/C4) | Low (consumed) |
| Anti-Sm | Specific for SLE |
Algorithm
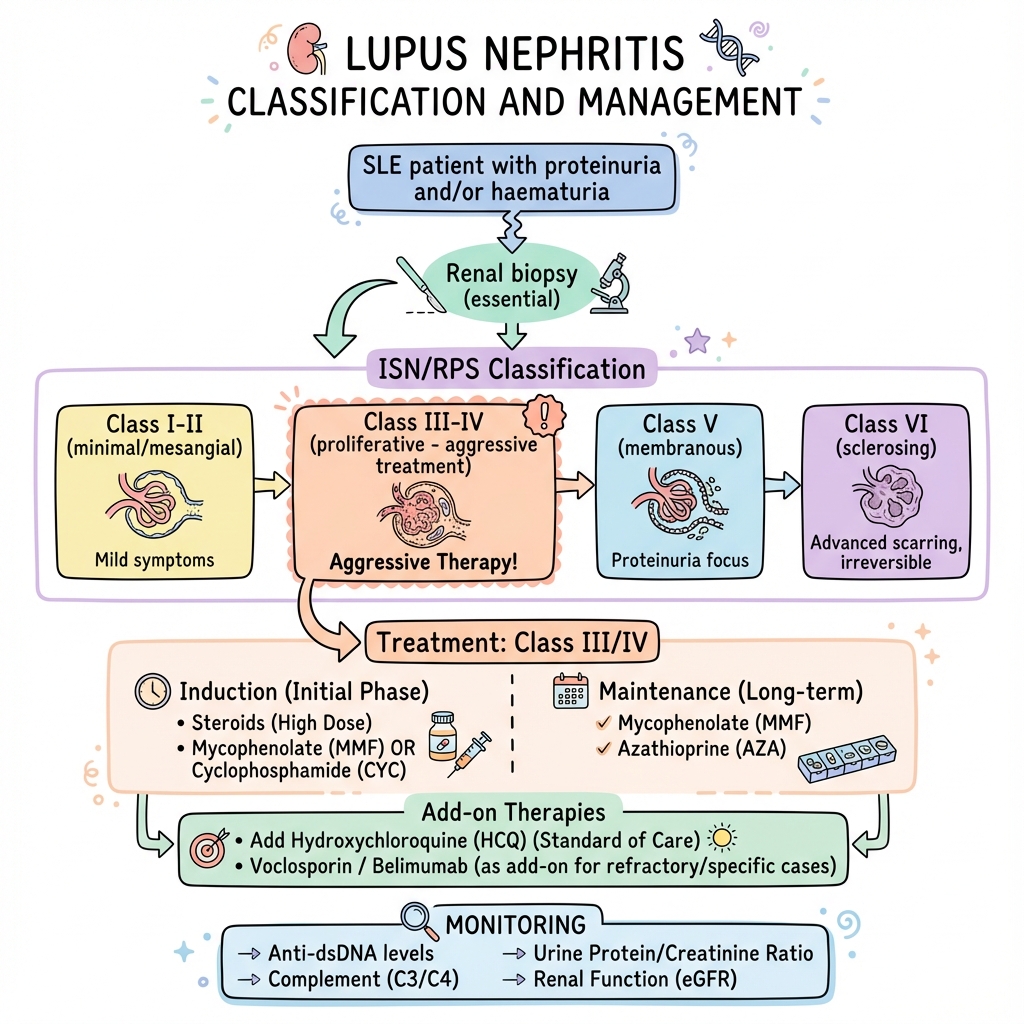
Induction (Class III/IV)
| Regimen | Notes |
|---|---|
| Steroids | IV methylpred then oral pred |
| Mycophenolate | 2-3g/day; preferred (ALMS trial) |
| Cyclophosphamide | Alternative; pulse IV (Euro-Lupus) |
Maintenance
| Drug | Duration |
|---|---|
| Mycophenolate | 1-2g/day; 3-5 years minimum |
| Azathioprine | Alternative |
Add-On Therapies
| Drug | Evidence |
|---|---|
| Hydroxychloroquine | Mandatory in all |
| Voclosporin | AURORA trial; added to MMF |
| Belimumab | BLISS-LN; added to standard therapy |
-
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Clinical Practice Guideline for Glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int Suppl. 2021. PMID: 34556256
-
Appel GB et al. Mycophenolate Mofetil versus Cyclophosphamide for Induction Treatment of Lupus Nephritis (ALMS). J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20(5):1103-1112. PMID: 19369404
-
Rovin BH et al. Voclosporin for Lupus Nephritis (AURORA). Kidney Int. 2021;99(3):698-709. PMID: 33272720
Viva Points
"Lupus nephritis affects 50% of SLE. Diagnose with renal biopsy (ISN/RPS). Treat Class III/IV with steroids + mycophenolate (ALMS). Add hydroxychloroquine always. Voclosporin (AURORA) and belimumab (BLISS-LN) are newer add-ons."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team