Acute Asthma
Summary
Acute asthma is a clinical emergency characterised by progressive worsening of asthma symptoms with increasing airflow obstruction. Severity is classified as moderate, severe, or life-threatening based on clinical features and peak flow. Management follows BTS/SIGN guidelines: high-flow oxygen, nebulised bronchodilators (salbutamol, ipratropium), systemic corticosteroids, and IV magnesium for severe/life-threatening attacks.
Key Facts
- Definition: Acute worsening of asthma requiring emergency treatment
- Incidence: Common; 1,200+ deaths/year in UK
- Pathognomonic: Wheeze + dyspnoea + reduced PEF
- Gold Standard Investigation: PEF, ABG if severe
- First-line Treatment: O2, nebulised SABA, steroids
- Prognosis: Good with prompt treatment; mortality less than 1%
Clinical Pearls
Severity Pearl: Unable to complete sentences = severe; silent chest = life-threatening.
Steroid Pearl: Oral steroids as effective as IV if patient can swallow.
Magnesium Pearl: Single dose 1.2-2g IV over 20 min for severe/life-threatening.
| Severity | Features |
|---|---|
| Moderate | PEF 50-75%, increasing symptoms |
| Severe | PEF 33-50%, unable to complete sentences, RR greater than 25, HR greater than 110 |
| Life-threatening | PEF less than 33%, silent chest, cyanosis, altered consciousness, exhaustion |
| Near-fatal | Raised PaCO2 and/or requiring mechanical ventilation |
Algorithm
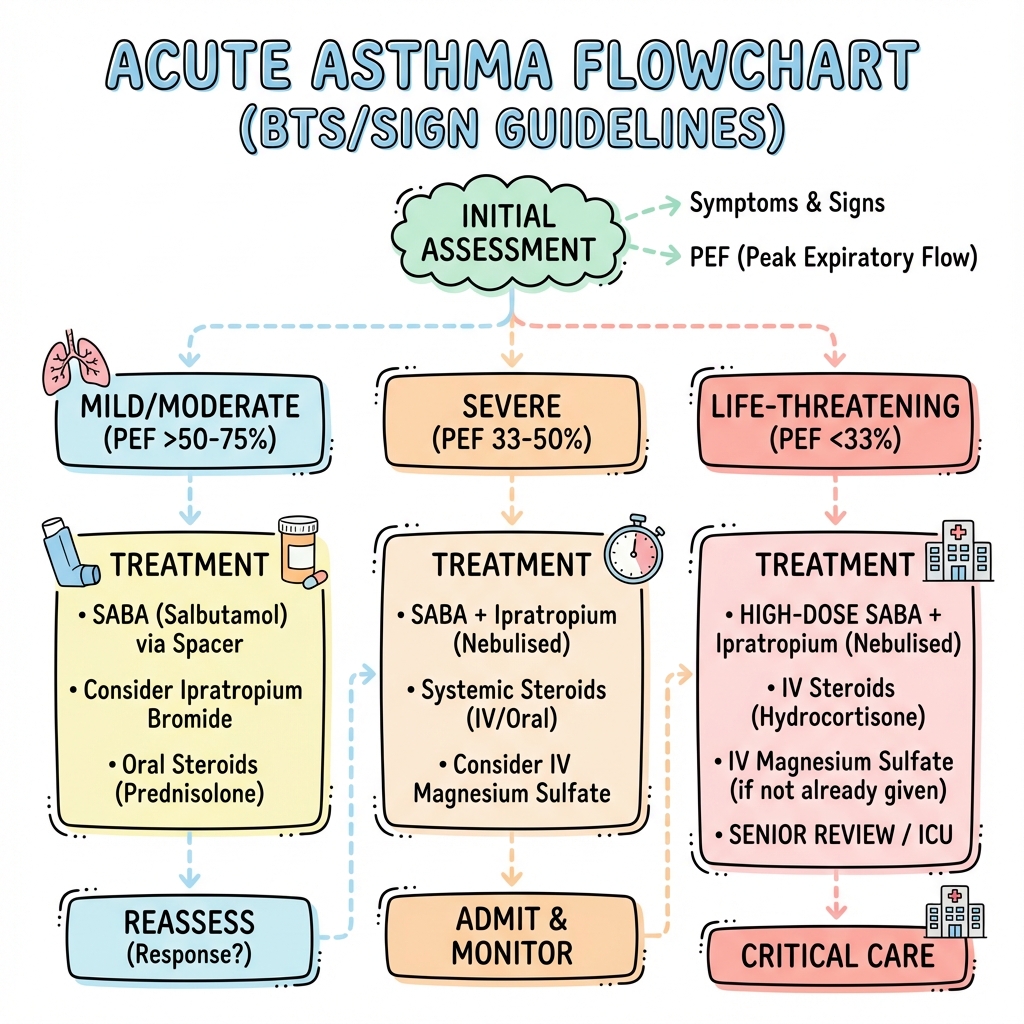
Treatment
| Intervention | Details |
|---|---|
| Oxygen | High-flow, target 94-98% |
| Salbutamol | 5mg neb, back-to-back if needed |
| Ipratropium | 500mcg neb added for severe |
| Steroids | Prednisolone 40-50mg PO or hydrocortisone 100mg IV |
| Magnesium | 1.2-2g IV over 20 min (severe) |
| Aminophylline | If not responding (monitor levels) |
-
BTS/SIGN. British guideline on the management of asthma. Thorax. 2019;74(Suppl 1):1-212. PMID: 31182536
-
NICE guideline NG80. Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic management. 2021.
Viva Points
"Acute asthma severity by PEF and clinical features. O2, nebs (SABA + ipratropium), steroids. IV magnesium for severe. Silent chest = life-threatening."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team