Acute Heart Failure
Summary
Acute heart failure (AHF) is rapid onset or worsening of heart failure symptoms requiring urgent therapy. Patients present with acute dyspnoea, orthopnoea, and signs of congestion (peripheral oedema, pulmonary crackles, raised JVP). Clinical profile classification (warm/cold, wet/dry) guides therapy. Initial management includes sitting upright, oxygen if hypoxic, IV loop diuretics, and vasodilators. Cardiogenic shock requires inotropes and potentially mechanical circulatory support.
Key Facts
- Definition: Rapid onset or worsening of HF symptoms
- Incidence: Common; leading cause of hospital admission over 65
- Pathognomonic: Acute dyspnoea + elevated BNP + congestion
- Gold Standard Investigation: BNP/NT-proBNP, Echo, CXR
- First-line Treatment: IV furosemide, oxygen, identify precipitant
- Prognosis: In-hospital mortality 5-10%
Clinical Pearls
BNP Pearl: BNP less than 100 or NT-proBNP less than 300 = HF very unlikely.
Profile Pearl: Warm/wet (most common) = diuretics + vasodilators. Cold/wet = inotropes.
Precipitant Pearl: Look for ACS, arrhythmia, infection, non-compliance.
| Profile | Features | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Warm/wet | Congested, well-perfused | Diuretics, vasodilators |
| Cold/wet | Congested, hypoperfused | Inotropes, consider MCS |
| Cold/dry | Hypoperfused, no congestion | Fluids, inotropes |
| Warm/dry | Neither | Optimise oral therapy |
Algorithm
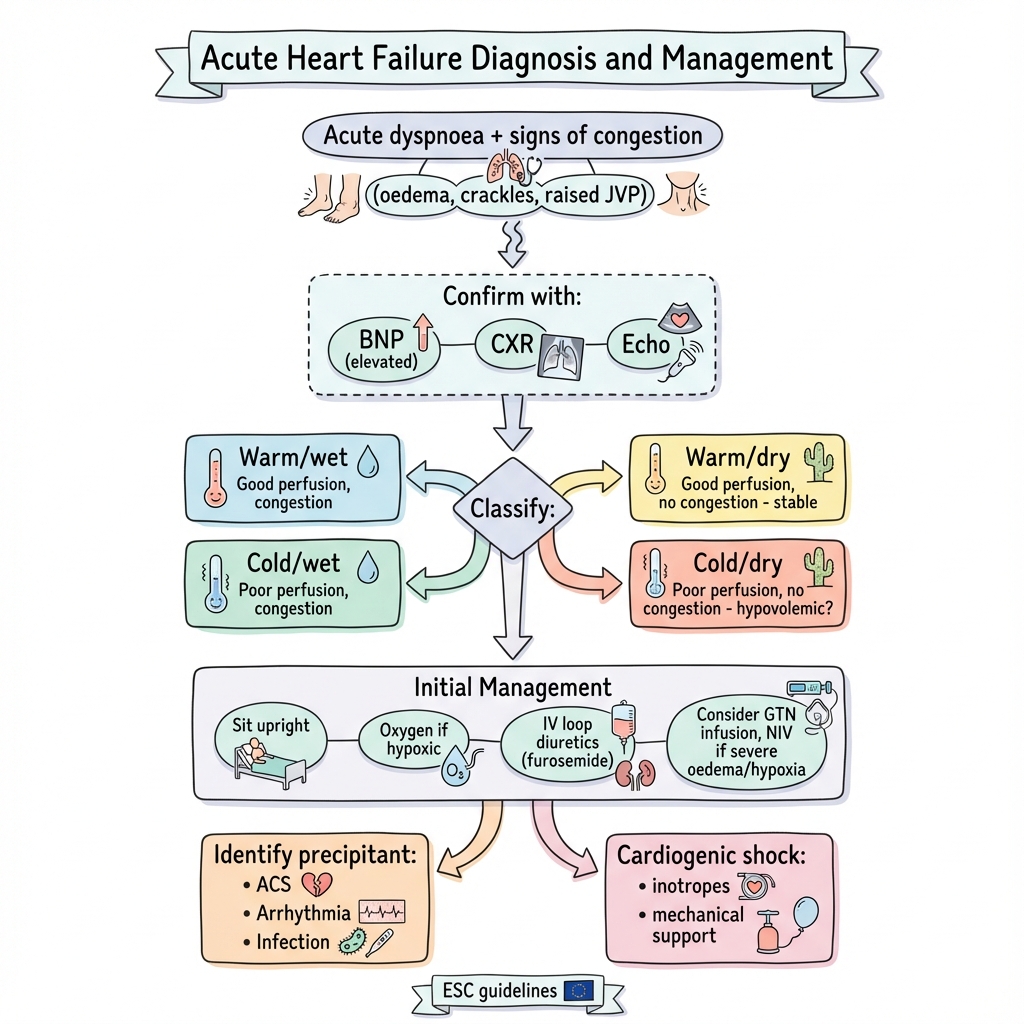
Initial Treatment
| Intervention | Details |
|---|---|
| Position | Sit upright |
| Oxygen | If SpO2 less than 90% |
| IV diuretic | Furosemide 40-80mg IV |
| Vasodilator | GTN infusion if hypertensive |
| NIV | CPAP/BiPAP if severe oedema |
Cardiogenic Shock
- Inotropes (dobutamine)
- Vasopressors if needed
- Mechanical support (IABP, Impella)
- McDonagh TA et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(36):3599-3726. PMID: 34447992
Viva Points
"AHF: acute dyspnoea + congestion. BNP elevated. Classify profile: warm/wet most common. IV furosemide first-line. Identify precipitant (ACS, arrhythmia). Cardiogenic shock = inotropes."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team