Behcet's Disease
Summary
Behcet's disease is a chronic, relapsing systemic vasculitis of unknown aetiology, characterised by recurrent oral and genital ulcers, ocular inflammation, and skin lesions. It can affect virtually any organ including the vascular system, CNS, and GI tract. Behcet's is more common along the ancient Silk Road (Turkey, Middle East, Japan). There is no diagnostic test; diagnosis is clinical based on International Criteria. Treatment is organ-based: colchicine for mucocutaneous disease, immunosuppression for organ-threatening manifestations, and anti-TNF agents for refractory cases.
Key Facts
- Definition: Systemic vasculitis with oral/genital ulcers and multi-organ involvement
- Incidence: Variable (highest in Turkey: 80-400 per 100,000)
- Peak Demographics: 20-40 years; slight male predominance (more severe in males)
- Pathognomonic: Recurrent oral ulcers (mandatory) + 2 of: genital ulcers, eye lesions, skin lesions, pathergy
- Gold Standard Investigation: Clinical criteria (no specific test)
- First-line Treatment: Colchicine; steroids + immunosuppression for severe
- Prognosis: Variable; ocular and neuro-Behcet's carry significant morbidity
Clinical Pearls
Diagnostic Pearl: Oral ulcers must be recurrent (at least 3 episodes in 12 months) to meet criteria.
Emergency Pearl: Posterior uveitis is sight-threatening - urgent ophthalmology referral and systemic immunosuppression.
Treatment Pearl: Infliximab is highly effective for severe/refractory disease.
| System | Manifestations |
|---|---|
| Oral | Painful recurrent aphthous ulcers |
| Genital | Ulcers (scrotum, vulva) - leave scars |
| Ocular | Anterior uveitis, posterior uveitis, retinal vasculitis |
| Skin | Erythema nodosum, papulopustular lesions, pathergy |
| Vascular | DVT, arterial aneurysms (pulmonary artery) |
| Neurological | Parenchymal (brainstem, meningoencephalitis), vascular (cerebral vein thrombosis) |
| GI | Ulceration (mimics IBD) |
Pathergy Test
- Skin hyperreactivity to minor trauma
- Papule/pustule at needle prick site after 24-48h
- 50-60% positive in endemic regions
| Test | Finding |
|---|---|
| HLA-B51 | Associated (not diagnostic) |
| CRP/ESR | Elevated during flares |
| Pathergy test | Positive in some |
| Ophthalmology | Slit-lamp, fundoscopy |
| MRI brain | If neuro-Behcet's suspected |
| CT angiography | If vascular involvement |
Algorithm
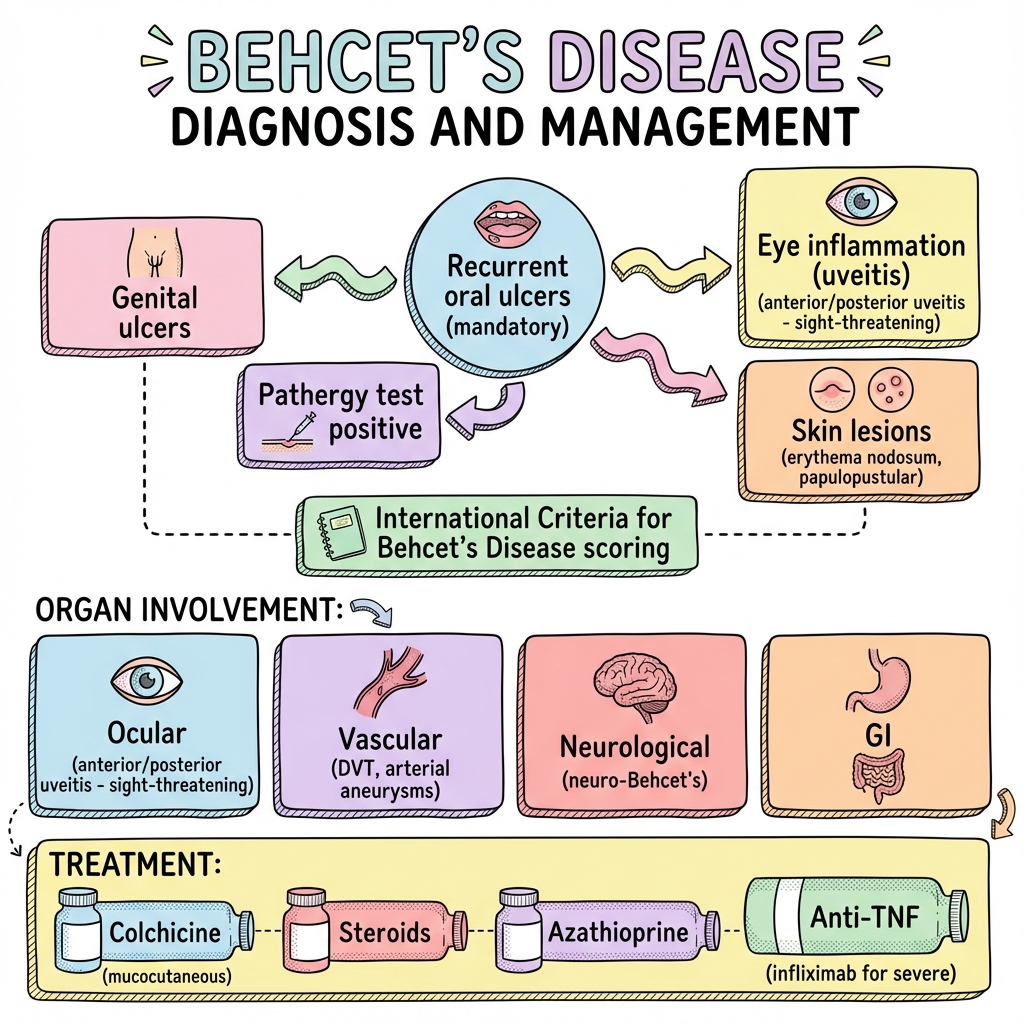
Mucocutaneous
| Drug | Notes |
|---|---|
| Colchicine | First-line for ulcers |
| Topical steroids | For ulcers |
| Azathioprine | Steroid-sparing |
| Apremilast | Oral ulcers (RELIEF trial) |
Ocular
| Drug | Notes |
|---|---|
| Systemic steroids | Initial control |
| Azathioprine/Cyclosporine | Maintenance |
| Infliximab | Sight-threatening uveitis |
| Interferon-alpha | Alternative |
Vascular/Neurological
- Steroids + immunosuppression
- Anti-TNF for refractory
- Anticoagulation controversial in venous disease
-
Hatemi G et al. 2018 Update of the EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Behcet's Syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(6):808-818. PMID: 29625968
-
Yazici H et al. Behcet Syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7(1):67. PMID: 34531387
Viva Points
"Behcet's is systemic vasculitis with recurrent oral ulcers + genital ulcers, uveitis, skin lesions. Diagnose clinically (ICBD criteria). Treat with colchicine for mucocutaneous; azathioprine/anti-TNF for ocular and organ-threatening disease."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team