Myxoedema Coma
Summary
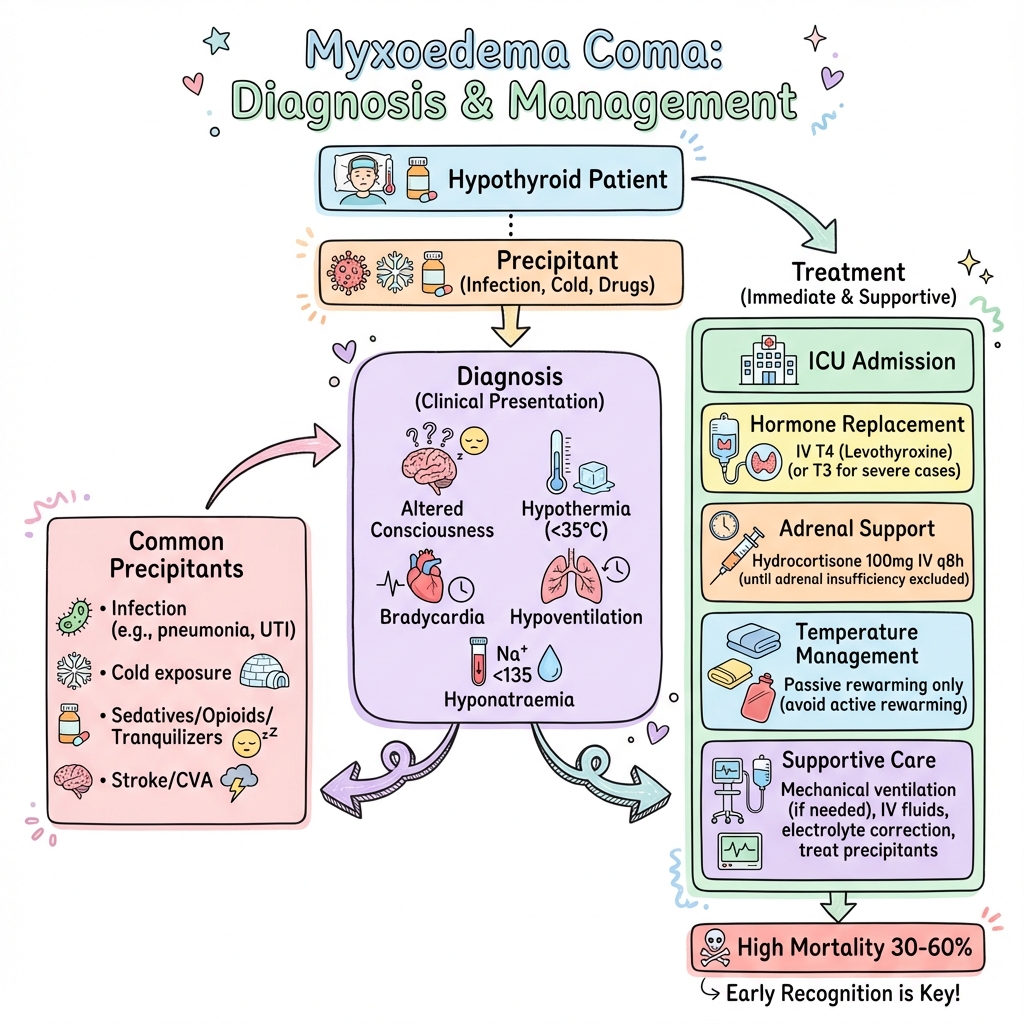
Myxoedema coma is a rare, life-threatening decompensation of severe hypothyroidism. Despite its name, patients are often obtunded rather than comatose. It typically occurs in elderly patients with undiagnosed or undertreated hypothyroidism after a precipitating event. Cardinal features include altered mental status, hypothermia, bradycardia, hypoventilation, and hyponatraemia. Treatment requires ICU admission, IV thyroid hormone replacement (T4 +/- T3), empirical hydrocortisone (to cover possible adrenal insufficiency), and supportive care. Mortality remains high at 30-60% even with treatment.
Key Facts
- Definition: Decompensated severe hypothyroidism with systemic failure
- Incidence: Very rare; peak in winter months
- Peak Demographics: Elderly women with undiagnosed/undertreated hypothyroidism
- Pathognomonic: Hypothyroidism + hypothermia + altered mental status
- Gold Standard Investigation: Clinical diagnosis + TFTs
- First-line Treatment: IV T4 +/- T3 + hydrocortisone + supportive
- Prognosis: Mortality 30-60%
Clinical Pearls
Emergency Pearl: Give hydrocortisone before or with thyroid hormone - thyroid replacement can precipitate adrenal crisis.
Temperature Pearl: Use passive rewarming only - active warming causes vasodilation and cardiovascular collapse.
Ventilation Pearl: Patients often have hypoventilation and CO2 retention - mechanical ventilation frequently required.
- Infection (most common)
- Cold exposure
- Sedatives, opioids
- Stroke
- Trauma
- GI bleeding
- Non-compliance with levothyroxine
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Mental status | Obtundation, confusion, coma |
| Temperature | Hypothermia (less than 35°C) |
| Cardiovascular | Bradycardia, hypotension, cardiomegaly |
| Respiratory | Hypoventilation, CO2 retention |
| GI | Ileus, ascites |
| Renal | Hyponatraemia (SIADH), renal impairment |
Algorithm
Thyroid Replacement
| Drug | Dose |
|---|---|
| Levothyroxine (T4) IV | Loading 300-500mcg, then 50-100mcg/day |
| Liothyronine (T3) IV | 5-20mcg then 2.5-10mcg q8h (severe cases) |
Glucocorticoids
| Drug | Dose |
|---|---|
| Hydrocortisone | 100mg stat then 50-100mg q8h |
Supportive Care
- ICU admission
- Mechanical ventilation if needed
- Passive rewarming (blankets only)
- Cautious IV fluids
-
Kwaku MP, Burman KD. Myxedema coma. J Intensive Care Med. 2007;22(4):224-231. PMID: 17712058
-
Wartofsky L. Myxedema coma. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2006;35(4):687-698. PMID: 17127141
Viva Points
"Myxoedema coma: altered mental status, hypothermia, bradycardia. Give steroids WITH thyroid hormone. Passive warming only. IV T4 +/- T3. High mortality."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team