Sepsis and Septic Shock
Summary
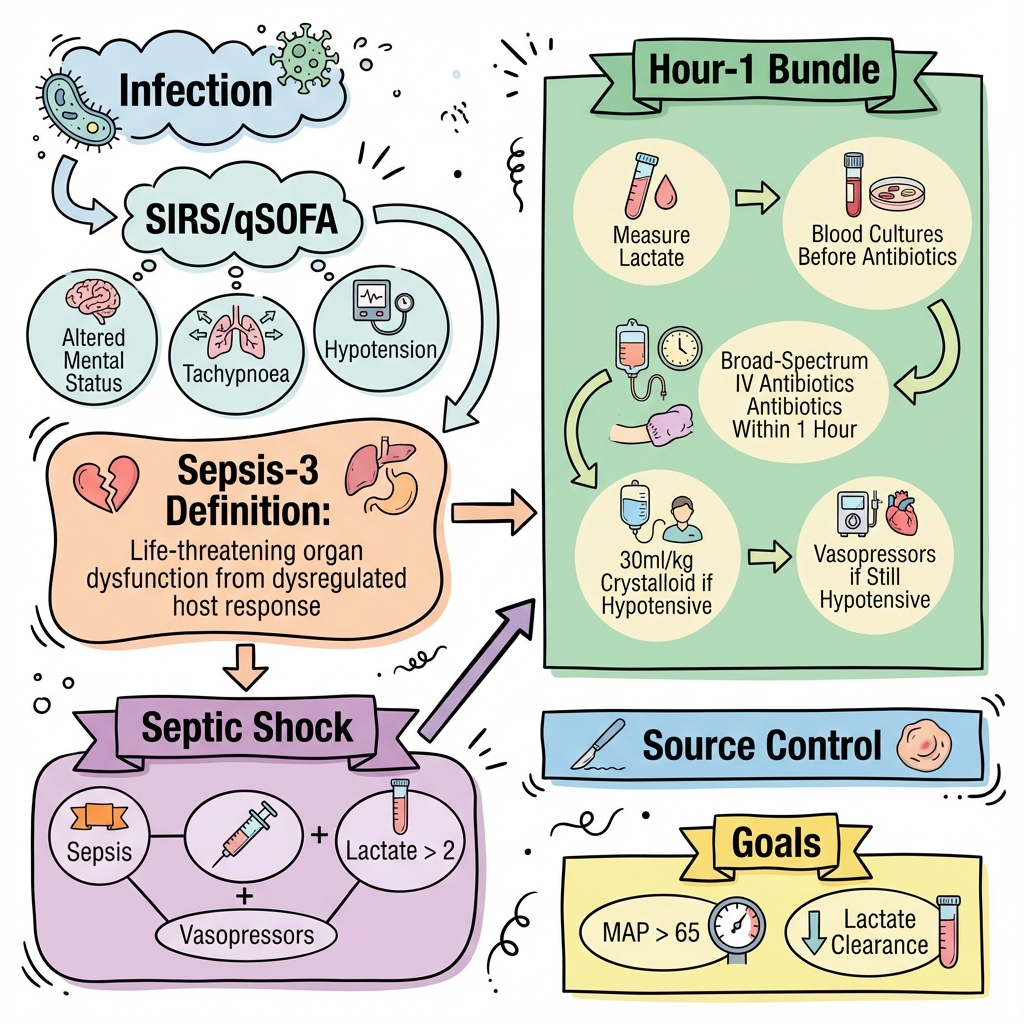
Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection (Sepsis-3 definition). Septic shock is sepsis with circulatory and metabolic abnormalities (vasopressor requirement to maintain MAP 65 or higher and lactate greater than 2 despite fluid resuscitation). Early recognition, rapid antibiotic administration, and goal-directed resuscitation are critical. The Surviving Sepsis Campaign provides evidence-based guidelines including the Hour-1 bundle for initial resuscitation.
Key Facts
- Definition: Organ dysfunction from dysregulated response to infection
- Incidence: 270 cases per 100,000; increasing
- Peak Demographics: Elderly, immunocompromised
- Pathognomonic: Suspected infection + organ dysfunction (qSOFA, SOFA)
- Gold Standard Investigation: Cultures, lactate, organ function tests
- First-line Treatment: Hour-1 bundle: cultures, antibiotics, fluids, vasopressors
- Prognosis: Sepsis 10% mortality; septic shock 40%
Clinical Pearls
Time Pearl: Each hour delay in antibiotics increases mortality.
qSOFA Pearl: qSOFA (RR 22+, SBP 100 or less, altered GCS) identifies high-risk patients at bedside.
Lactate Pearl: Lactate greater than 4 mmol/L = high risk even if normotensive.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Sepsis | Infection + organ dysfunction (SOFA 2+) |
| Septic shock | Sepsis + vasopressors for MAP 65+ AND lactate greater than 2 |
qSOFA (Screening)
- Altered mental status
- RR greater than or equal to 22
- SBP less than or equal to 100
| Action | Details |
|---|---|
| Measure lactate | Remeasure if greater than 2 |
| Blood cultures | Before antibiotics |
| Antibiotics | Broad-spectrum within 1 hour |
| Fluids | 30ml/kg if hypotensive or lactate 4+ |
| Vasopressors | If hypotensive after fluids |
Algorithm
Resuscitation
| Intervention | Target |
|---|---|
| Fluids | 30ml/kg crystalloid |
| Noradrenaline | First-line vasopressor |
| MAP | Greater than or equal to 65 mmHg |
| Lactate | Clear to normal |
Source Control
- Drain abscesses
- Remove infected devices
- Debride necrotic tissue
-
Singer M et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016;315(8):801-810. PMID: 26903338
-
Evans L et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines 2021. Intensive Care Med. 2021;47(11):1181-1247. PMID: 34599691
Viva Points
"Sepsis-3: organ dysfunction from infection. Septic shock = vasopressors + lactate greater than 2. Hour-1 bundle: lactate, cultures, antibiotics within 1h, 30ml/kg fluids, vasopressors. Target MAP 65."
Last Reviewed: 2026-01-01 | MedVellum Editorial Team